
Microsoft's Data Execution Prevention
Data Execution Prevention (DEP) is a set of hardware and software technologies that perform additional checks on memory to help prevent malicious code from running on a system. In Microsoft Windows XP Service Pack 2 (SP2) and Microsoft Windows XP Tablet PC Edition 2005, DEP is enforced by hardware and by software.
The primary benefit of DEP is to help prevent code execution from data pages. Typically, code is not executed from the default heap and the stack. Hardware-enforced DEP detects code that is running from these locations and raises an exception when execution occurs. Software-enforced DEP can help prevent malicious code from taking advantage of exception-handling mechanisms in Windows.
In some regions, they are disabling DEP by default at the time of the OS build. That can be done by setting one of these two values in the c:\boot.ini (hidden file). This requires a reboot of the server.
/noexecute=OptIn
or
/noexecute=AlwaysOff
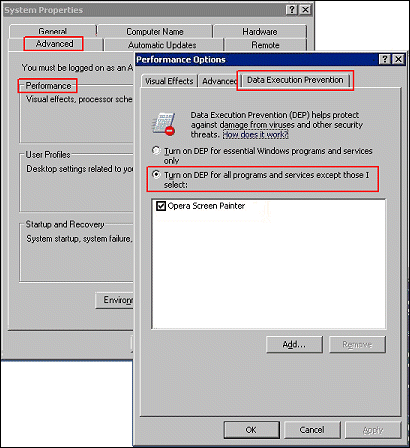
The other option is to allow Screen Painter to bypass DEP. (Other programs may also need to be given the same access.) This is done by the following process.
See Also