
ORMS Configuration Miscellaneous
Note: This topic applies to ORMS ADF11.
Access the Miscellaneous Dashboard by selecting Configuration>Miscellaneous. The Miscellaneous Dashboard configuration allows users to set internal system parameters that are used for Optimization, such as:
Also, Reservation Ratios are important to the modeling of the business forecast and are necessary for accurate forecasting calculations.
Details are described in the following sections.
In a multi-property environment with more than one modeled or pre-modeled property, the Property LOV displays in the Title Bar ![]() . Users with access rights and permissions to other properties can select the LOV and choose either the modeled or pre-modeled property they want to work with. The sections on the dashboard refresh data specific to the selected property. In a single property environment or in a multi-property environment where the user has rights to only one property, the property field is read-only.
. Users with access rights and permissions to other properties can select the LOV and choose either the modeled or pre-modeled property they want to work with. The sections on the dashboard refresh data specific to the selected property. In a single property environment or in a multi-property environment where the user has rights to only one property, the property field is read-only.
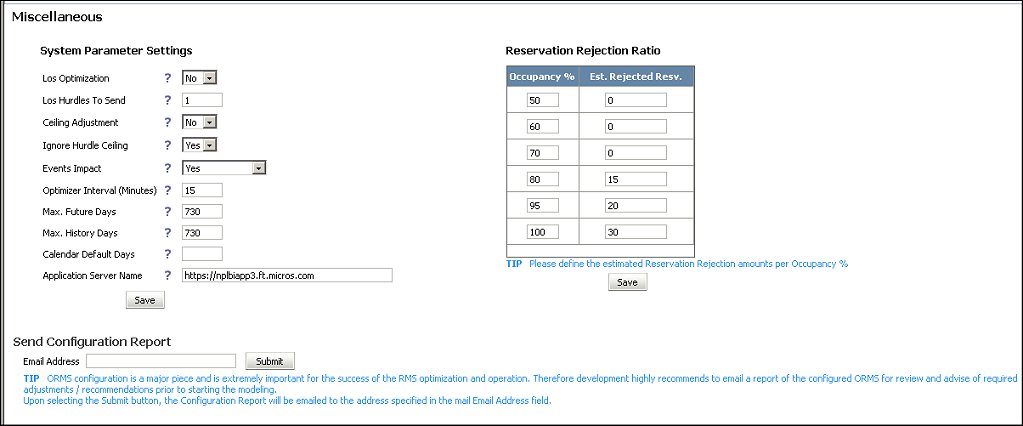
Select the system parameter settings or enter the reservation rejection ratio that you would like used for ORMS. The following text describes each field.
Question Mark/Help icon. During the process of entering parameters if you need an explanation of the fields, select the Question Mark/Help icon ![]() for informational prompts. The following field Explanations are identical to the Help prompts in the application.
for informational prompts. The following field Explanations are identical to the Help prompts in the application.
ORMS CRO. If an ORS license is active in the database, enter the CRO code that ORMS needs to initialize with.
If no ORS license is active, the value ‘CRO’ displays by default.
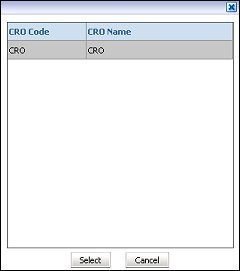
Explanation: When ORMS is installed in an ORS environment, the CRO code that the ORMS UI needs to initialize with needs to be entered. If ORMS is installed in a PMS environment, the default value 'CRO' must be used.
LOS Optimization. Select which Optimization process you want to use. The default value is No which will result in Stay Date Optimization (LOS=0). Select Yes if you want full LOS Optimization (LOS1 up to LOS7, depending on Max LOS) for arrivals.
Explanation: This parameter will allow the hotel to have hurdles calculated based on Stay Date Hurdles only. If the parameter is set to No, ORMS will only calculate Stay Date (LOS=0) hurdles and all LOS1 to LOS7 will be calculated in the back-end based on each day's LOS0, which means that OPERA will still get up to LOS7 hurdles. Switching this parameter off (No) is very useful for hotels with a majority of short stay, i.e. 1 or 2 nights, rather than 5-6 nights.
Note: When changing this parameter from Yes to No or from No to Yes after the system has already been modeled, you must remodel the system. See ORMS Configuration Verification.
- When changing LOS Optimization from Yes to No, or vice versa (No to Yes), in a modeled, running environment ORMS will stop the optimizer and delete existing hurdle rates. Then, the optimizer will restart without user intervention and apply the new hurdle calculations, update the hurdles in OPERA, and take alerts and hurdle schedules into consideration. If there is an error in this process, an Error Message will display indicating the action to take.
- When LOS Optimization is set to N, Alerts for LOS >1 are not triggered or displayed on the Alerts and Events screen. When set to Y (LOS1 to LOS7), then Alerts for LOS=0 are not triggered or displayed on the Alerts and Events screen.
LOS Hurdles to Send. Available when LOS Optimization is set to No and Prevailing Rates are inactive, enter the number (1-7) of hurdles to send to PMS.
Note: Prevailing Rates need to be inactive for the LOS Hurdles to Send field to display because Prevailing Rates requires 7 LOS Hurdles to be sent.
Explanation: With this parameter, the property can specify the number the hurdles (LOS1-LOS7) for each room type and day for PMS Configuration, resulting in a cutback of OXI messages that get sent out of system.
Ceiling Adjustment. The default Yes results in ORMS calculating the Hurdle ceiling adjustments based on historical RevPAR for economy analysis. If No is selected, no ceiling adjustments based on historical RevPAR for economy analysis will be performed.
Explanation: When active, ORMS calculates the Hurdle ceiling adjustment based on historical RevPAR for economy analysis.
Ignore Hurdle Ceiling. When Ignore Hurdle Ceiling is set to "Yes," ceiling will continue to be calculated and displayed as today; however, the hurdle step calculation will not be limited by the ceiling as today. The "Max Hurdle" column will display on the Hurdle Recommendations screen when this parameter is set to "Yes."
When Ignore Hurdle Ceiling is set to "No," the Max Hurdle column will not display and the functionality will remain the same as today, but the hurdle is limited to the ceiling.
Events Impact. Select whether you want ORMS to calculate the impact of the RMS events or not. Setting this option to No or <No Selection>, the system will still consider event dates in history calculation but doesn't count their impact separately. The default is <No Selection>.
Explanation: This flag identifies if the system needs to calculate the impact of the events or not. Setting it to No or Null (No Selection) still considers event dates in history calculation but doesn't count the impact separately. When setting this parameter to Yes, it is recommended to group events with similar impact in order to have more historical dates.
Optimizer Interval (Minutes). Enter the value in minutes to set the interval in which the Optimizer Service will run.
Explanation: When left blank or set to anything below 15, the Optimizer Interval will be 15 minutes, as this is the minimum Interval time. If set to anything above 15, this value determines the minutes of the interval in which the Optimizer Service will run.
Max. Future Days. Enter the number of days into the future for which you would like the system to calculate Forecast and Hurdles. The default value is set to one year (365 days). In an already modeled environment, the parameter values can only be increased from the current value. In an environment prior to modelization, the parameter values can either be increased or decreased from the current value.
Note: When changing this parameter after the system has already been modeled, you must remodel the system. See ORMS Configuration Verification.
Explanation: This parameter determines the future days until we calculate Forecast and Hurdles. The default value is set to 1 year (365 days) and the maximum value is 2 years (730 days). Changing this parameter value after the system has been modeled will require a re-modeling.
Max. History Days. Enter how many days in the past you want the system to access data to calculate Forecast and Hurdles. The default value is set to two years past (730 days). In an already modeled environment, the parameter values can only be increased from the current value. In an environment prior to modelization, the parameter values can either be increased or decreased from the current value.
Note: When changing this parameter after the system has already been modeled, you must remodel the system. See ORMS Configuration Verification.
Explanation: This parameter determines how far back in the past we look to calculate Forecast and Hurdles. The default value is set to 2 years (730 days) and the maximum value is 4 years (1460 days). Changing this parameter value after the system has been modeled will require a re-modeling.
Calendar Default Days. To provide more flexibility, you may define the default time period that will initially appear on the Home Dashboard. The default value is two weeks (14 days). You may change the dates from one day to 31 days, by entering the amount (1-31) in the field. The first day will be the PMS business date. When you make changes, log out and log in again and you will see the new values on the Home Dashboard.
Explanation: This parameter determines the number of days that will be selected by default in ORMS screens' calendar. The default value is set to 14 days.
Application Server Name. The name of the application server where the reports are published.
ORMS uses the reservation rejection ratio to calculate unconstrained demand. (i.e., how many reservations would be booked if the hotel were to accept all reservations, regardless of the minimum hurdle setting.)
Using the Reservation Rejection Ratios configuration, a Revenue Manager can enter the estimated number of reservations the hotel rejects based on occupancy percentages. For example, a hotel might reject reservations that do not meet the minimum hurdle. (i.e., the cost the hotel would incur if it were to accept that reservation. Examples of these costs include housekeeping cost, room maintenance cost, etc.)
The unconstrained demand is calculated at the time of modeling for past dates.
To get the unconstrained demand, we first calculate the rejected demand for each booking class and add that value to the actual yieldable reservations for the booking class. This gives us the adjusted actual reservations count (i.e., unconstrained demand). The unconstrained demand is then used to forecast the hurdle amount for future reservations, with the goal to get the highest RevPAR possible.
Example:
For this example, we will use a past date: 1-JAN-2010.
The hotel has a total of 110 rooms, out of which 10 rooms were OOO on 1-JAN-2010.
The rooms booked for yieldable reservations were 80.
Occupancy pct = ( 80 / (110 - 10) ) * 100 = 80%
We will assume the rejected reservations count estimate is 50 for 70% occupancy. To calculate the rejected demand per booking class, we take the ratio of actual reservations per each booking class and multiply that ratio by the number of rejected reservations.
Example:
The DELUXE, GRAND and SUITE booking classes are configured.
DELUXE = 40 reservations.
GRAND = 20 reservations.
SUITE = 20 reservations.
To get the rejected demand for DELUXE, we calculate as follows:
Take the ratio of the reservations of DELUXE over the total reservations in the hotel and multiply that ratio by the estimate of the rejected reservations count.
(40 / 80) * 50 = 25.
Note: The unconstrained demand for DELUXE was 40 + 25 = 65.
In this section, you will enter the estimated Reservation Rejection amounts based on each Occupancy % at your property. This information is used for forecasting.
Occupancy %. The various percentages of occupancy for the property used for forecasting (along with the associated estimated rejection ratio, see below). The default Occupancy % values are generated when ORMS is activated (30/50/70/80/90/100).
Note: It is not recommended that you change the default Occupancy % values. If it is necessary to change the default values, however, do not enter duplicate numbers in the grid (i.e. do not enter 50 in the second field and 50 in the third or fourth fields, etc.).
Est. Rejection. Resv. Type in the estimated reservation rejection based on the Occupancy % for the property. Ask yourself," based on the occupancy percentage, how many reservations will not be allowed and need to be turned away?" For example, if your property has 30% occupancy there may be 0 rejections. If your property has 100% occupancy you may have an estimated 15 reservations rejected.
As the Miscellaneous Tab is the last part of the Configuration process, the current configuration of ORMS can be emailed to a recipient to review and confirm that all of the configuration has been setup correctly. The recipient of this report would be an ORMS Expert, such as the Implementation Representative or Development, so that the report can be reviewed and any feedback for adjustments can be responded back to the installer/property. Once the adjustments/feedback have been reviewed by the installer, they can then discuss them with the property and then continue with the Modeling.
Email Address. Enter the email address of the recipient that needs to review the ORMS Configuration Report and click on the Submit button. Once the Submit button is selected, the report will then be send to the specified recipient as several HTML files.
Note: For this functionality to work properly, the Email Delivery functionality needs to be configured. See Email Delivery Configuration for details.
The following is the Tip that is displayed under the Email Address field:
ORMS configuration is a major piece and is extremely important for the success of the RMS optimization and operation. Therefore development highly recommends to email a report of the configured ORMS for review and advise of required adjustments / recommendations prior to starting the modeling.
Upon selecting the Submit button, the Configuration Report will be emailed to the address specified in the mail Email Address field.
The following are examples of the reports that are sent. Click on them to view a sample PDF of the report.
Note: All of the reports will always be sent, regardless if the application parameter for its functionality is set to Yes or No. For example, if the Reservations>Reservation Upsell application function is set to N for the property, the Upsell Configuration report will still be created but will contain no data.
See Also
Show Me
![]() Emailing the ORMS Configuration Report
Emailing the ORMS Configuration Report